Composite Pattern
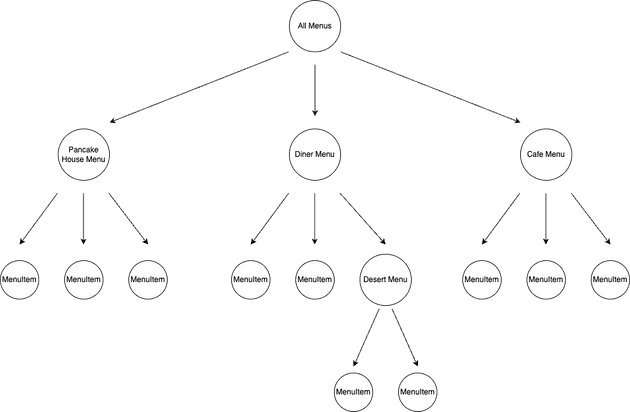
어떤 식당에서 판매하고 있는 메뉴들을 담는 Menu 객체가 있다.
그리고 실제 품목을 의미하는 MenuItem 객체가 있고, Menu 객체 안에서는 MenuItem을 Collection으로 담고 있다고 해보자.
public class PancakeHouseMenu implements Menu {
private final ArrayList<MenuItem> menuItems;
public PancakeHouseMenu() {
menuItems = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
menuItems.add(menuItem);
}
}그런데 여기서 메뉴 내부에 존재하는 서브 메뉴를 추가해서 아래와 같이 계층 구조로 표현해야하는 요구사항이 생겼다.
public class DinerMenu implements Menu {
private final List<MenuItem> menuItems = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<Menu> menus = new ArrayList<>();
public void addItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
menuItems.add(menuItem);
}
public void addMenu(Menu menu) {
menus.add(menu);
}
}위 코드로도 계층적인 구조를 표현할 수 있다.
하지만 문제점이라고 하면 addMenu 메서드가 추가되어 메뉴에 새로운 것을 추가하는 행위가 2가지로 구분되었다는 것이다.
이는 만약 메뉴 내부의 요소들을 가져온다거나, 메뉴 내용을 출력한다거나 하는 새로운 기능이 필요할 때 항상 MenuItem과 Menu 두 객체 모두 고려하여 구현해야 한다.
이는 클라이언트 입장에서는 각 메뉴는 아이템과 서브 메뉴로 구성되어 있음을 알고 적절한 메서드를 호출해줘야함을 의미한다.
여기서 컴포지트 패턴을 적용할 수 있다.
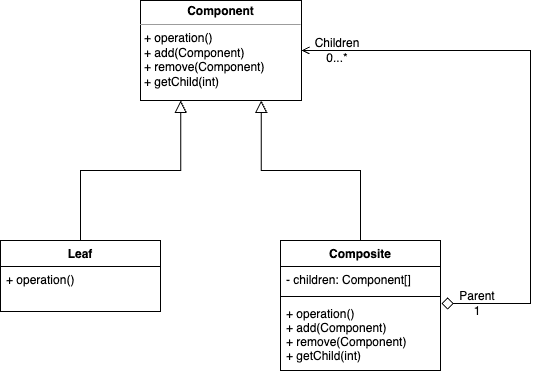
컴포지트 패턴 또한 트리 구조를 사용하여 계층 구조를 표현하는 패턴이다.
그런데 여기서 추가적으로 복합 객체(e.g. Menu)와 개별 객체(e.g. MenuItem)을 동일한 인터페이스로 처리하여 같은 방법으로 다룰 수 있는 part-whole hierachy를 구성한다.
해당 패턴을 통해 구현하면 클라이언트 입장에서 Menu와 MenuItem을 별개로 취급하지 않아도 된다.
패턴 적용
public interface MenuComponent {
default void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default String getName() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default String getDescription() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default double getPrice() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default boolean isVegetarian() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default void print() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}public class Menu implements MenuComponent {
private final List<MenuComponent> menuComponents = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
private final String description;
public Menu(String name, String description) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
@Override
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.add(menuComponent);
}
@Override
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.remove(menuComponent);
}
@Override
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
return menuComponents.get(i);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.print("\n" + getName());
System.out.println(", " + getDescription());
System.out.println("---------------------");
Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = menuComponents.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuComponent menuComponent = iterator.next();
menuComponent.print();
}
}
}public class MenuItem implements MenuComponent {
private final String name;
private final String description;
private final boolean vegetarian;
private final double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
@Override
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
@Override
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.print(" " + getName());
if (isVegetarian()) {
System.out.print("(v)");
}
System.out.println(", " + getPrice());
System.out.println(" -- " + getDescription());
}
}public class Waitress {
private MenuComponent allMenus;
public Waitress(MenuComponent allMenus) {
this.allMenus = allMenus;
}
public void printMenu() {
allMenus.print();
}
}구현을 살펴보면 MenuComponent는 Menu, MenuItem의 기능 모두를 정의하고 있다.
명백한 단일 책임 원칙의 위반이지만 이같은 경우 원칙을 포기한 대신, 클라이언트에서 하나의 인터페이스로 모두 처리할 수 있도록 투명성을 확보한 경우로 볼 수 있다.
따라서 Menu 객체에서 MenuItem에 사용되는 메서드를 클라이언트에서 호출하는 등 안정성이 떨어질 수는 있다.
참고
- 에릭 프리먼, 엘리자베스 롭슨, 키이시 시에라, 버트 베이츠, 헤드 퍼스트 디자인 패턴, 서환수, 한빛미디어
- https://github.com/bethrobson/Head-First-Design-Patterns