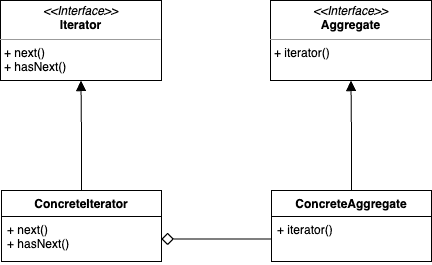
Iterator Pattern
반복자 패턴은 데이터 집합의 구현 방법을 직접적으로 노출하지 않으면서 항목들을 순회하는 방법을 제공해준다. 데이터 집합이 배열로 구현되어 있던, Collection의 List나 Set, Map으로 구현되어 있던 일관된 방식으로 사용할 수 있게 된다.
식당에서 판매하는 메뉴를 나타내는 클래스가 있고, 팬 케이크를 취급하는 메뉴와 다이너에서 취급하는 메뉴를 나타내는 클래스가 있다고 해보자.
두 클래스 모두 MenuItem을 통해 메뉴를 취급한다.
public class MenuItem {
private final String name;
private final String description;
private final boolean vegetarian;
private final double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
}public class PancakeHouseMenu {
private final ArrayList<MenuItem> menuItems;
public PancakeHouseMenu() {
menuItems = new ArrayList<MenuItem>();
addItem(
"K&B's Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with scrambled eggs and toast",
true,
2.99
);
addItem(
"Regular Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with fried eggs, sausage",
false,
2.99
);
addItem(
"Blueberry Pancakes",
"Pancakes made with fresh blueberries and blueberry syrup",
true,
3.49
);
addItem(
"Waffles",
"Waffles with your choice of blueberries or strawberries",
true,
3.59
);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
menuItems.add(menuItem);
}
public ArrayList<MenuItem> getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
}public class DinerMenu {
private static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6;
private int numberOfItems = 0;
private final MenuItem[] menuItems;
public DinerMenu() {
menuItems = new MenuItem[MAX_ITEMS];
addItem(
"Vegetarian BLT",
"(Fakin') Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
true,
2.99
);
addItem(
"BLT",
"Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
false,
2.99
);
addItem(
"Soup of the day",
"Soup of the day, with a side of potato salad",
false,
3.29
);
addItem(
"Hotdog",
"A hot dog, with sauerkraut, relish, onions, topped with cheese",
false,
3.05
);
addItem(
"Steamed Veggies and Brown Rice",
"A medly of steamed vegetables over brown rice",
true,
3.99
);
addItem(
"Pasta",
"Spaghetti with Marinara Sauce, and a slice of sourdough bread",
true,
3.89
);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
if (numberOfItems >= MAX_ITEMS) {
System.err.println("Sorry, menu is full! Can't add item to menu");
} else {
menuItems[numberOfItems] = menuItem;
numberOfItems = numberOfItems + 1;
}
}
public MenuItem[] getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
}만약 이 두 가게가 합병되어 모든 메뉴를 한 번에 다뤄야한다면 어떻게 될까?
PancakeHouseMenu의 ArrayList<>를 반환하고 있고, DinerMenu에서는 MenuItem[]이라는 배열을 반환하고 있다.
클라이언트에서 이들을 모두 순회하려면 리스트의 순회 방법과 배열의 순회 방법 모두를 파악해서 아래와 같이 순회하는 수 밖에 없다.
List<MenuItem> pancakeMenus = pancakeHouseMenu.getItems();
for (int i = 0 ; i < pancakeMenus.size() ; i++) {
MenuItem menuItem = pancakeMenus.get(i);
...
}
MenuItem[] dinerMenus = dinerHouseMenu.getItems();
for (int i = 0 ; i < dinerMenus.length ; i++) {
MenuItem menuItem = dinerMenus[i];
...
}클라이언트를 배려하기 위해서는, 메뉴의 집합을 저장하는 실제 구현체와는 무관하게 캡슐화하여 일관된 방법을 제공하는 것이 좋다. 그리고 이 반복 작업을 캡슐화하는 방법이 바로 반복자 패턴이 된다.
패턴 적용
public interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
MenuItem next();
}반복자 인터페이스는 보통 다음 요소가 존재하는지 확인하는 hasNext() 메서드와 다음 요소를 반환하는 next() 메서드로 이루어진다.
직접 정의해서 사용해도 되나 언어 차원에서 지원하는 경우가 많으며 자바에서는 java.util.Iterator를 제공하고 있다.
특히, Collection의 경우에는 이미 메서드를 제공하기에 별도 구현 없이 Iterator를 그냥 받아 사용할 수 있다.
흔히 사용하는 enhanced-for 구문이나 Collection의
forEach메서드도 이를 기반으로 한다. 엄밀히 말하면 Collection 객체는Iterator를 반환하는 메서드를 가진Iterable을 구현한다.
public class DinerMenuIterator implements Iterator<MenuItem> {
private final MenuItem[] list;
private int position = 0;
public DinerMenuIterator(MenuItem[] list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public MenuItem next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return list[position++];
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return position < list.length && list[position] != null;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
if (position <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("You can't remove an item until you've done at least one next()");
}
if (list[position - 1] != null) {
if (list.length - 1 - (position - 1) >= 0)
System.arraycopy(
list,
position - 1 + 1, list,
position - 1,
list.length - 1 - (position - 1)
);
list[list.length - 1] = null;
}
}
}그리고 각 식당의 메뉴를 나타내는 클래스는 인터페이스를 추가하여 적용한다.
public interface Menu {
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator();
}public class DinerMenu implements Menu {
private static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6;
private int numberOfItems = 0;
private final MenuItem[] menuItems;
...
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator() {
return new DinerMenuIterator(menuItems);
}
}public class PancakeHouseMenu implements Menu {
private final ArrayList<MenuItem> menuItems;
...
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator() {
return menuItems.iterator();
}
}참고
- 에릭 프리먼, 엘리자베스 롭슨, 키이시 시에라, 버트 베이츠, 헤드 퍼스트 디자인 패턴, 서환수, 한빛미디어
- https://github.com/bethrobson/Head-First-Design-Patterns